Selecting 3D Scanning Technology
Blog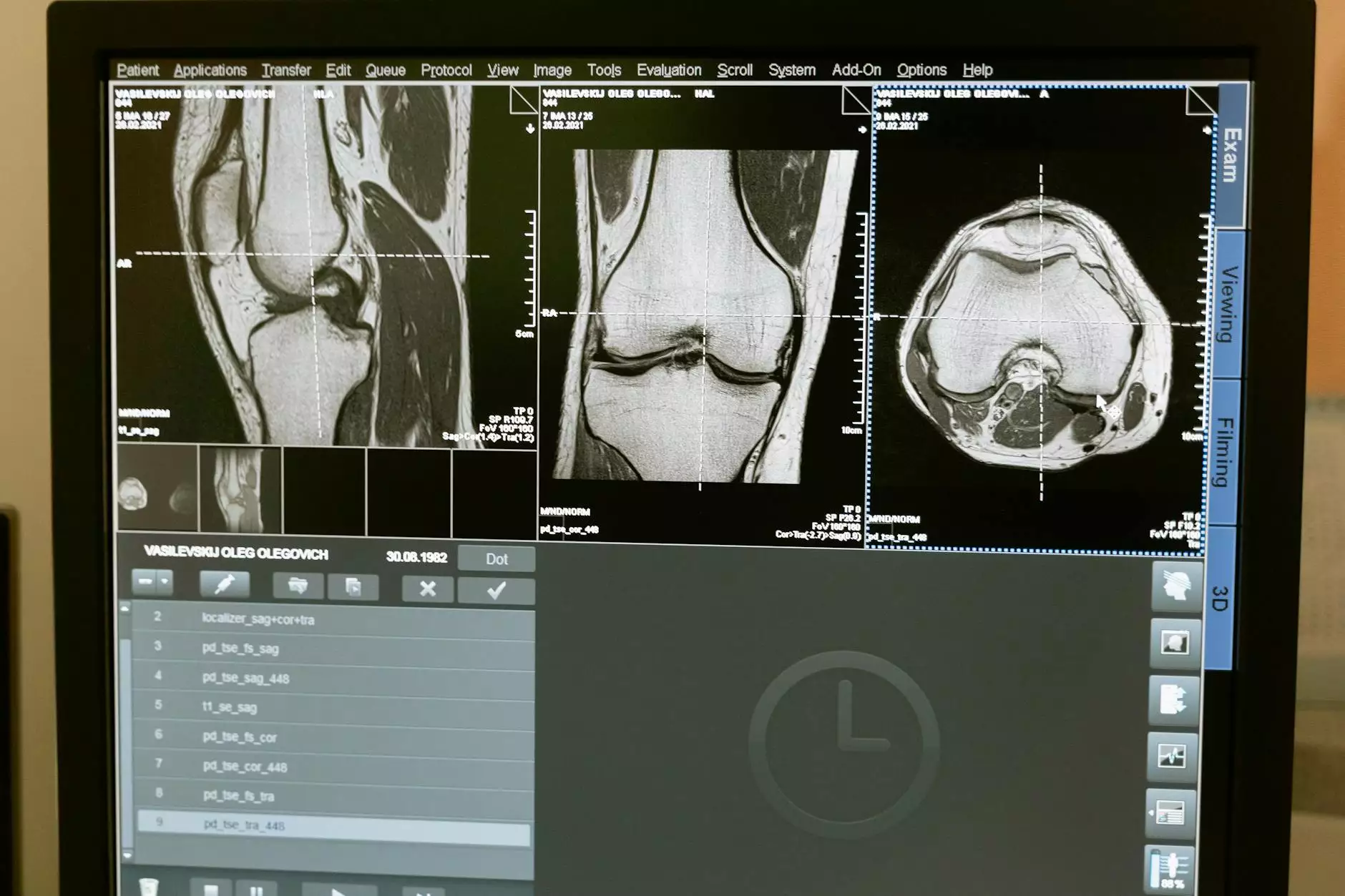
Introduction
Welcome to RPM Design and Prototype, your trusted partner in innovative design and rapid prototyping solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of 3D scanning technology and help you understand how to select the right technology for your specific requirements. Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, medical, or any other industry, 3D scanning technology can revolutionize your workflow and drive efficiency.
Why Choose 3D Scanning Technology?
Before delving into the various 3D scanning techniques and considerations, let's understand why 3D scanning technology is gaining popularity across industries.
- Accurate Replication: 3D scanning allows you to capture intricate details of physical objects with exceptional accuracy, ensuring precise replication in virtual environments.
- Time and Cost Savings: By enabling quick and non-destructive capturing of objects, 3D scanning reduces the time and cost associated with traditional measurement and modeling methods.
- Enhanced Design Iterations: 3D scanning facilitates the rapid development of prototypes, enabling designers and engineers to iterate and refine their designs faster.
- Quality Control: With 3D scanning, you can perform detailed inspections, identify anomalies, and ensure consistent quality across your production lines.
- Reverse Engineering: Reverse engineering becomes seamless with 3D scanning, allowing you to analyze and recreate existing objects, components, or parts.
Types of 3D Scanning Techniques
There are various 3D scanning techniques available, each suited for specific applications and object characteristics. Let's explore some of the common techniques:
Laser Triangulation
Laser triangulation is a popular technique where a laser light projects a pattern onto the object's surface, capturing the distortion to determine its shape and create a 3D representation.
Structured Light Scanning
Structured light scanning involves projecting a series of patterns onto the object's surface. The distortions caused by the patterns are then analyzed to generate accurate 3D representations.
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry utilizes multiple photographs taken from different angles to create a 3D model. Advanced algorithms analyze the photos and extract 3D data based on corresponding points.
Contact Scanning
Contact scanning is ideal for capturing small, intricate objects. It involves physically probing the object's surface and recording the spatial coordinates to build a precise 3D model.
X-Ray or CT Scanning
X-ray or CT scanning techniques are used when non-destructive inspection or scanning of the internal structure is required, allowing for detailed analysis and measurements.
Considerations for Selecting the Right Technology
Choosing the appropriate 3D scanning technology for your specific needs requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Object Size and Detail
Different scanning techniques have limitations regarding the size and level of detail they can capture. Determine the size and intricacy of your objects to select a compatible scanning technology.
Speed and Efficiency
If you require fast scanning or automated data capture, consider technologies that offer high-speed scanning capabilities or integrate with automation solutions.
Accuracy Requirements
Consider the level of accuracy needed for your applications. Some industries demand sub-millimeter precision, while others may be more forgiving in terms of accuracy requirements.
Material Compatibility
Ensure that the scanning technology you choose is compatible with the materials commonly used in your industry. Certain materials may require specific scanning techniques.
Workflow Integration
Evaluate how the scanning technology integrates into your existing workflow. Compatibility with your design software, ease of data transfer, and compatibility with downstream processes are crucial considerations.
Budget and ROI
Consider your budget and the return on investment (ROI) you expect from implementing 3D scanning technology. A balance between cost, functionality, and future benefits is essential.
Conclusion
3D scanning technology unlocks a world of possibilities in design, prototyping, quality control, and reverse engineering. By understanding the different scanning techniques and considering various factors, you can confidently select the right technology for your specific needs. RPM Design and Prototype is dedicated to delivering cutting-edge solutions, leveraging our expertise in 3D scanning technology, and ensuring your success in the ever-evolving landscape of product design and development.